Back pain comes in many forms and variations. Localization and nature of pain, duration, presence or absence of radiation to other parts of the body, provoking factors - all this can be combined in various combinations.Back pain in the shoulder blade area- a common type of pain in various diseases.
The main cause of pain in the shoulder blades and back
Why does my back hurt in the shoulder blade area?Such symptoms can be observed in diseases of the spine, neurological disorders, pathologies of muscles and other organs. These include referred pain in pulmonary and heart diseases, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as pain in radicular syndromes, trauma, and osteochondrosis. Let's take a closer look at the common causes of pain in the back and shoulder blades.
Injury
Injury to the scapula occurs in two ways - with direct impact (bump, fall) and indirectly, with load along the axis of the upper limb (fall on the elbow, sharp contraction of the muscles of the shoulder girdle). In the first case, simultaneous spinal injury and rib fracture are possible. Such injuries occur in 50% of serious traffic accidents. Severe pain, limited mobility, and severe swelling of the tissue around the shoulder blade may also occur with severe bruising.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a common causeback painAndspineany localization, and also inshoulder blade area. Degenerative-dystrophic processes in the joints and intervertebral discs, resulting from malnutrition and cartilage regeneration, lead to the formation of protrusions and hernias, back muscle spasms, and a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs. Spinal nerves may be pinched; pain may be caused by radicular syndrome.
The pain is triggered by bending or twisting the body, lifting weights. Due to concomitant inflammation of the back muscles, pain may increase when lifting and abducting the arm. Possible stiffness of the spine, stoop, forced position of the patient with a slight bend forward. The pain can be aching, stabbing, encircling the chest. Some patients describe it by saying that they feel like something is stuck between their shoulder blades.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a disease in which pathological S-shaped curvature of the spine occurs, especially in the coronary plane. As a result, load distribution and normal biomechanics are disrupted. Predisposing factors for scoliosis are incorrect body posture, weak back muscles, childhood, and inappropriate workplace settings. Back pain from scoliosis is usually caused by spasm, inflammation, and tension in muscles that are unable to support and stabilize a weakened spine.
Scoliosis is characterized by aching pain that disappears when lying down and gets worse when standing for a long time.
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a pathological curvature of the spine in the sagittal plane, most often occurring in the thoracic region. As a result of kyphosis, the spine begins to resemble a question mark "? ", and the formation of a hump may begin. Predisposing factors for kyphosis are vitamin D deficiency, osteoporosis, and poor posture. Kyphosis can be caused by trauma or tuberculosis of the spine. Ankylosing spondylitis causes extreme kyphosis of the thoracic region.
Pain in kyphosis, like scoliosis, is caused by muscle tension and spasm, due to excessive stress. At the same time it is feltback muscle painand in the regionshoulder blade
Spondyloarthritis, spondyloarthritis
Spondyloarthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic change in the intervertebral joints, caused by malnutrition of the articular cartilage, leading to gradual destruction of the spinal joints. Spondyloarthritis is inflammation of the intervertebral joints that occurs in response to an autoimmune or reactive process (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis). The result of both processes is ankylosis or fusion of the intervertebral joints, which causes impaired mobility of the spine. The difference is that in the first case, the inflammation is secondary and occurs in response to joint damage, while in the second case, the primary inflammation causes degenerative-dystrophic changes.
Pain in spondyloarthritis and spondyloarthrosis is aching and increases at night. Typical symptoms are stiffness and stiffness in the spine in the morning, which disappears after gymnastics or physical activity. The course of the disease is chronic, undulating, with periods of exacerbation and improvement. The pain can be localized not only between the shoulder blades, but throughout the spine.
Bulges and hernias
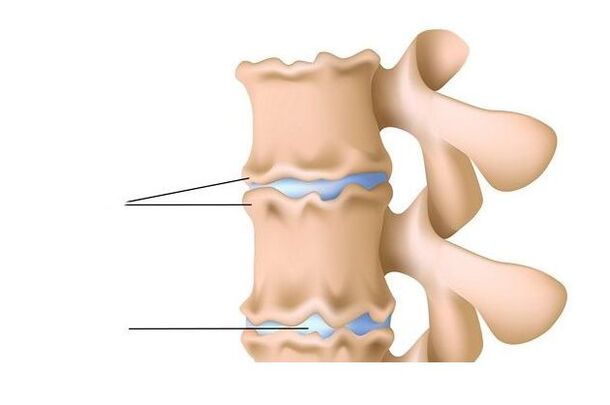
Protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs are the result of advanced spinal osteochondrosis. The intervertebral discs, which have lost their elasticity and elasticity, or rather their peripheral parts, called fibrous rings, bulge under the influence of loads and form protrusions. If the annulus fibrosus ruptures, the inner contents of the disc fall out, forming a disc herniation. Protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs can cause entrapment of the spinal cord roots that emerge through the intervertebral foramina. Acute pain, protective tension and muscle spasms occur. The pain can radiate to the shoulder, elbow, forearm, and is often localized in the area of the shoulder blade (with a hernia or protrusion in the thoracic spine).
Radiculitis
Acute pain that begins in the interscapular area and continues along the intercostal spaces is the most common sign of sciatica. This is caused by compression of the spinal nerves by herniation or protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Less commonly, sciatica may be caused by a tumor, spondylosis, or displacement of the vertebrae. A typical sign of this disease is pain triggered by movement in the thoracic spine and lifting heavy objects.
Humeroscapular periarthrosis
Humeroscapular periarthrosis is a disease accompanied by pain in the shoulder and shoulder blade, caused by arthrosis of the shoulder joint and inflammation of the surrounding soft tissues. Predisposing factors include injuries and microtrauma of the shoulder joint, intense physical activity in athletes and workers, and osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine. Humeral periarthrosis is the most common cause of acute pain in the shoulder blade and shoulder joint.
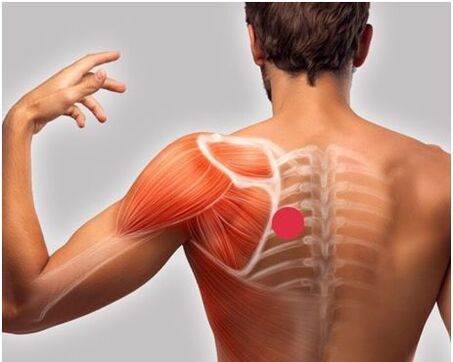
Pain occurs gradually, aggravated from episodic pain during physical activity, with a wide range of motion in the shoulder joint (swinging the arm, throwing, when placing the arm behind the back). Then the pain becomes constant, even at rest. Therefore, the patient cannot sleep on the affected side.Pain inshoulders andgive back to the shoulder blades. Possible stabbing pain when moving. Characterized by a sharp limitation of mobility in the shoulder joint, the patient is unable to raise or abduct his arm.
Nerve pain
Pain in the shoulder blade area, radiating along the intercostal nerves, is a sign of neuralgia, a chronic nerve disease. The typical symptom is increased pain when coughing, sneezing, or moving—the pain becomes sharp and shooting. The cause of this disease is irritation of the roots of the spinal cord due to spinal diseases, spondyloarthritis and spondyloarthrosis, muscle inflammation. Exacerbations can be triggered by drafts, hypothermia and physical exertion.
Heart disease
Cardiac pathology is often accompanied by severe pain in the area of the left shoulder blade. The causes of pain syndrome can be angina pectoris, coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels. Severe acute pain under the left shoulder blade that does not go away for a long time is a sign of myocardial ischemia or infarction. The nature of the pain varies - from aching, constant, to acute, with shooting pain in the left shoulder and forearm, neck on the left. Typical symptoms are pain relief with nitrates (drugs for the treatment of heart failure) - nitroglycerin, isoket, nitrosorbide.
Problems with the digestive tract
Gastrointestinal diseases are a common cause of back pain in the shoulder blade area. Pain is reflected naturally, and occurs because some of the pain impulses from the solar plexus and receptors in the digestive tract return to the spinal cord. Pain in the area of the shoulder blade can occur with hiatal hernia, chronic or acute pancreatitis, gastric ulcer, and duodenal ulcer. For cholecystitis and gallstonespainfullocalizedbehind between the shoulder blades, Againon the right.
Lung disease
Pain in the shoulder blades can occur with a number of diseases of the lungs and bronchi. Most often these are pneumonia, acute bronchitis, asthma and other pathologies. Lung cancer sufferers oftenback pain in the area of the shoulder blades.
Areas of back pain in the area of the shoulder blades
Pain in the area of the shoulder blades when inhaling or exhaling is a typical sign of intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis of the spine with protrusion or herniation of the intervertebral disc, inflammation of the back muscles, and radiculitis. The reason for the pain is that the act of breathing is carried out through the coordinated contraction of a large number of muscles, and movement even at such a volume can provoke increased pain in the above diseases.
Pain in the sternum and shoulder blades
Pain in the sternum and scapula is often found in glenohumeral periarthrosis. Inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic changes in the shoulder joint disrupt the normal distribution of loads, which is why pathological changes begin at the site of attachment of the clavicle and ribs to the sternum (Tietze syndrome).
Pain in the sternum and shoulder blades also occurs in lung and heart diseases.
Pain in the right or left shoulder blade
Pain in the left shoulder blade can be a reflection of heart disease, as mentioned above. Pain in the right shoulder blade is characteristic of acute or chronic cholecystitis, gallstones.
Pain in the shoulder blades and neck
Back pain,in the area of the shoulder blades and neckpossibly with osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine. This symptom is also characteristic of a hernia or bulge. Referred pain in the neck and shoulder blades is observed in some diseases of the heart and lungs (angina pectoris, lung cancer, pneumonia).
Types of pain in the shoulder blades
Pain in the shoulder blade
Pain in the shoulder blade on the left is observed with heart disease, on the right - with diseases of the biliary tract, gallstone disease. Aching pain accompanied by glenohumeral periarthrosis, neuralgia, and radiculitis. Pain in the back and in the area of the shoulder blades is also possible with spondyloarthritis and spondyloarthrosis.
Pressing pain in the shoulder blades
Tenderness in the shoulder blade is a characteristic of myositis or inflammatory muscle disease. The shoulder blade is surrounded by a series of muscles, inflammation of which causes not only pain, but also limited mobility of the shoulder girdle. Severe inflammation of the soft tissues and ligaments of the shoulder joint may also be accompanied by pain.
Dull pain when inhaling
Dull pain in the back and shoulder blades, aggravated by inhalation, can be observed with pneumonia, lung cancer, neuromuscular pathology and myositis. This symptom is also a sign of injury, back bruising, and soft tissue hematoma. Dull pain in the back and shoulder blades is accompanied by some diseases of the spinal cord, such as multiple sclerosis.
Throbbing pain in the shoulder blade
Throbbing pain in the shoulder blades, which is aggravated by movement, sneezing and coughing, is a sign of back injuries, fractures and cracks in the shoulder blades. The mechanism of injury is most often a direct physical impact or an indirect impact transmitted along the axis of the upper extremity, for example when falling on the elbow.
When moving (walking) pain in the shoulder blades
Pain in the shoulder blades when walking can occur with hernias and protrusion of the thoracic spine. The axial load on the spine that occurs when moving and striking the ground with the heel is transferred to the diseased intervertebral disc and triggers pain.
Burning sensation in the shoulder blade area
A burning sensation in the area of the shoulder blade is a possible sign of acute myocardial infarction. Ischemia (circulatory failure and lack of oxygen in the heart muscle) of the myocardium is accompanied by severe pain, painful shock and a decrease in blood pressure. However, if the posterolateral wall of the left ventricle and the septum of the heart are damaged, pain can resemble spinal osteochondrosis, poor-quality food poisoning, acute surgical pathology and many other diseases.
Burning and tingling of the skin in the interscapular area may be a symptom of a hernia or protrusion of the intervertebral discs in the thoracic and cervical spine. This symptom occurs in multiple sclerosis and other spinal cord diseases.
Shoulder pain and nausea
Pain in the left shoulder blade accompanied by nausea and vomiting may also indicate acute myocardial infarction. Similar symptoms are characteristic of acute cholecystitis, gallstones, obstructive jaundice (blockage of the lumen of the bile ducts with stones) - pain is more localized on the right, nausea is caused by intoxication.
How to relieve pain in the shoulder blades
For spinal diseases and many other diseases, pain relief is facilitated by rest and bed rest. An effective way to treat pain is to prescribe analgesics, especially non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, dry heat, distraction and anti-inflammatory agents in the form of ointments and gels on the skin help. Patches with anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used, their effect is limited to the area of application and is not accompanied by significant side effects.

It is important to remember that any pain is an indication to consult a doctor. This is because long-term use of analgesics increases the risk of serious and dangerous complications. Therefore, its use as a treatment is aimed at relieving pain before visiting a doctor. Once the cause is determined, treatment is tailored to the diagnosis and individual characteristics of the patient.
How to diagnose pain in the shoulder blade?
To diagnose the causes of pain in the shoulder blades, a clinical examination by a doctor is used, which allows one to identify mild symptoms and signs that are characteristic of a particular disease. A study of skin sensitivity, reflex testing, assessment of range of motion in the shoulder joints and spine, etc. is carried out. To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental methods such as ECG, ultrasound, CT or MRI are used.

Magnetic resonance imaging is a universal method for diagnosing the causes of back pain associated with pathologies of the spine, spinal cord, joints and soft tissues. This procedure is safe, highly accurate, and allows you to obtain detailed images of the desired area. This method is based on the physical phenomenon of magnetic resonance, which is created using only a magnetic field and radio waves, which is safe for human health.
Treatment of shoulder blade pain
Treatment of pain in the back and shoulder blades is aimed at the cause of the disease (etiotropic treatment), the mechanism of occurrence (pathogenetic treatment), and symptoms (symptomatic treatment). The treatment plan depends on the patient's diagnosis and condition. As an example, consider a treatment plan for spinal osteochondrosis.
To eliminate degenerative-dystrophic phenomena and improve the nutrition of the soft tissues of the spine, chondroprotectors, vitamin therapy, drugs that improve blood microcirculation, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy are prescribed. To relieve tension in the back muscles, massage is performed and muscle relaxants are prescribed. When a herniated spinal nerve is pinched, physical influences are used - underwater traction, manual therapy. To overcome pain, analgesics are prescribed.
Treating shoulder blade pain at home
Home treatment is possible only if the patient has consulted a doctor, undergone an examination, during which an accurate diagnosis has been established. In most cases, the causes of pain in the shoulder blades and back do not require urgent hospitalization, treatment is carried out at home, according to the doctor's prescription. However, what happens more often is the opposite - patients try to be treated at home, engage in self-diagnosis and use painkillers uncontrollably. The result of self-diagnosis and self-medication is chronic pain and analgesic side effects. Patients often come to the doctor late when their disease causes complications. In case of serious illness, late treatment significantly worsens the prognosis and reduces the chances of a complete cure. That is why back pain requires careful diagnosis and consultation with a doctor.
Which doctor should I consult for shoulder blade pain?

By clarifyingcauses and treatment of pain in the shoulder blades and backtreated by a neurologist, since in most cases the pain syndrome is neurogenic in origin. These are almost all diseases of the spine, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Spinal injuries are treated by a traumatologist, but in this case, if neurological symptoms are present, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. In extreme cases, if you have back pain, you should at least contact a therapist so that he can establish a preliminary diagnosis and refer the patient to consult another specialist. The worst thing is if the patient does not see a doctor and self-medicates - the consequences of such "treatment" lead to complications, chronic diseases, and in some cases pose a threat to human health and life.



















































