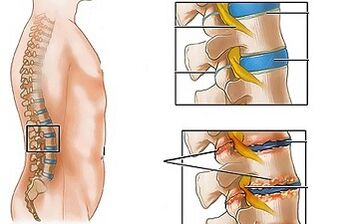
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that develops as a result of the degenerative-distribution process in intervertebral discs.This disease is widespread and affects in most cases, people aged 25 to 40 years.
According to back pain statistics, at least once in their lives every adult experienced, while in 95% of their cases are caused by osteochondrosis spine.
Patients with severe lumbar osteochondrosis, with persistent pain and other manifestations are recognized as temporary defects.If within four months their condition does not improve, the problem of formation of disability groups is resolved.
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a serious medical and social problem, because this disease mainly affects people from the most working age, and in addition, in the absence of treatment, it can cause the formation of intervertebral disk hernias.
Causes and risk factors
Factors that are predisposing for the development of lumbar osteochondrosis are:
- spinal structure abnormalities;
- Lumbarization is a congenital pathology of the spinal cord, characterized by the separation of the first vertebrae sacrum and transformation in the sixth lumbar (additional);
- Sacralization is a innate pathology, where the fifth lumbar vertebra is fed with sacrums;
- asymmetrical location of intervertebral joint articular cracks;
- pathological narrowing of the spinal canal;
- Spondiogenic pain that is reflected (somatic and muscle);
- obesity;
- lifestyle that does not move much;
- Prolonged vibrational exposure;
- Systematic physical tension;
- smoke.
Hazing statodynamic loads combined with one or more risk factors cause changes in the physiological properties of nucleus jackets from fibrous discs, play a role that absorbs shock and provides mobility of the spinal column.The basis of this process is the polysaccharide depolymerization, which causes loss of moisture with a jet nucleus cloth.As a result, the nucleus of the jacket, and with that, fibrous disks lose their elastic nature.Further mechanical load provokes fibrous ring protrusions that have lost elasticity.This phenomenon is called bulge.Cracks appear in the core of fibrous, where the jacket nucleus fragments (prolapse, hernias from intervertebral discs) fall.
The long compression of the nervous roots that instead of certain organs from the abdominal cavity from time to time causes a decrease in function.
The instability of the spinal segment is accompanied by reactive changes in the adjacent vertebral body, intervertebral joint, and spondy arthrosis together develop.Significant muscle contraction, for example, with a background of physical activity, causes a shift in the vertebral body and violation of nerve roots with the development of radicular syndrome.
Osteofit can be another cause of pain and neurological symptoms with lumbar osteochondrosis - bone growth in the vertebral process and body that causes Royshold syndrome or compression myelopathy (spinal cord compression).
Form of disease
Depending on which structure is drawn into the pathological process, clinically clinically lumbar osteochondrosis is manifested by the following syndrome:
- Reflex- Lumbalgia, Lumbohachalia, Lumbago;developing against the background of the reflex voltage from the back muscles;
- compression (spine, vascular, radicular)- Their development leads to compression (compression) spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots.Examples are lumbosacral radiculitis, radiculoichemia.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
With lumbar osteochondrosis, symptoms are determined by the structure drawn into the pathological process.
Lumbago occurs under the influence of hypothermia or physical voltage, and sometimes without clear reason.The pain suddenly appeared and shot.This increases when sneezing, coughing, body turns, physical activity, chair, standing, walking.In a lying position, pain significantly weakens.Sensitivity and reflexes are maintained, the volume of movement in the lumbar area is reduced.
About palpation, they observe:
- pain in the lumbar area;
- paravertebral muscle spasms;
- Leveling lordosis lumbar, which in many cases is combined with scoliosis.
Nerve root voltage syndrome with negative lumbar.When lifting straight legs, the patient records an increase in pain in the lower back, and not their appearance in the elongated lower leg.
Often, with lumbar osteochondrosis, there is a recurring pain attack, which every time becomes more intense and long.
With lumbaria, clinical images resemble lumbago, however, increased pain intensity occurs within a few days.
In lumbar shaped, the patient complains of pain in the lower back, which radiates to one or both lower limbs.The pain spread over the buttocks and the back of the thighs and never reached the feet.
Vasomotor disorders are lumbar -shaking characteristics:
- changes in temperature and color of the lower extremity skin;
- hot or cold feeling;
- Violation of blood supply.
The development of clinical lumbar compression syndrome is manifested by the following symptoms:
- dermatomic gipalgesia;
- Shooting pain;
- Weakening or loss of deep reflexes;
- Peripheral paresis.
With compression syndrome, pain increases when tilting the body, sneezing and coughing.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis is based on the clinical picture of the disease, laboratory, and instrumental research methods.
In a blood test with a background of lumbar osteochondrosis, it can be noted:
- decreased calcium concentration;
- Increased ESR;
- Increase the level of alkaline phosphatase.
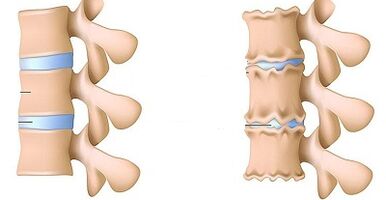
In diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis, the radiological examination of the spine is given very important.
The long compression of the nervous roots that instead of certain organs from the abdominal cavity from time to time causes a decrease in function.
The X -Ry feature that confirms the diagnosis is:
- changes in the configuration of the affected segment;
- pseudospondylaastez (related vertebral body shift);
- deformation of the closing plate;
- alignment of intervertebral disk;
- High intervertebral disk height (symptoms of spacer), which is associated with asymmetrical muscle tone.
Also in the diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis with indications used:
- Myelography, Computed or Magnetic Refusal Tomography - needed for persistent symptoms, the development of neurological deficiency;
- Scintegraphy (study of the accumulation of phosphorus bone systems, liquid-99 technology)-is carried out in cases of suspicion of tumors or infectious processes, spinal injuries.
The differential diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis is done with the following diseases:
- Spondylolistz;
- spondylopathy disgormonal;
- ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- Infectious process (inflammatory disk, spinal osteomyelitis);
- non -plastic process (spinal primary tumor or metastasis lesion);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- deformation of osteoarthrosis hip joint;
- Reflected pain (internal organs and large blood vessels).
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
With lumbar osteochondrosis, they usually comply with the following treatment tactics:
- Bed rest for 2-3 days;
- traction of the affected spinal segment;
- strengthen the back muscles and abdominal press (creation of muscle corset called SO);
- Impact on the Myofascial and Pathological myofascial processes.
Lumbago occurs under the influence of hypothermia or physical voltage, and sometimes without clear reason.
In most cases, conservative treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out, including the following steps:
- muscle infiltration with local anesthetic solutions;
- Take anti -inflammatory non -steroidal drugs;
- Acceptance of Desensitization Agents;
- Vitamin Therapy;
- acceptance of sedatives and antidepressants;
- manual therapy, massage;
- Physiotherapy Physical Education;
- acupuncture;
- Posisometric relaxation.
Absolute indications for the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis surgery are:
- Acute or subacute compression of the spinal cord;
- The development of a ponytail syndrome, characterized by disorders of the function of pelvic organs, sensitive and motor disorders.
Medical Gymnastics for Lumbar Osteochondrosis
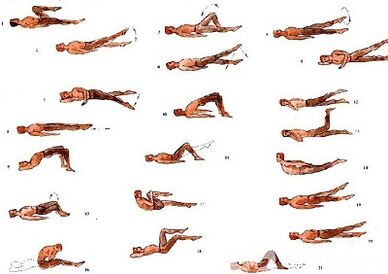
In the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis complex, important roles include physiotherapy exercises.Regular classes make it possible to normalize paravertebral muscle tone, increase the metabolic process in tissue that is influenced by pathological processes, and besides forming muscle corset that are well developed, which can maintain the spine in the correct position, eliminate excess static loads from it.
So that gymnastics with lumbar osteochondrosis to bring the biggest effect to comply with the following principles:
- Class order;
- gradual increase in the intensity of physical activity;
- Avoid excessive work during the lesson.
Physical education must be involved in the leadership of experienced instructors, who will choose the most effective exercise for certain patients and control the truth of their implementation.
According to back pain statistics, at least once in their lives every adult experienced, while in 95% of their cases are caused by osteochondrosis spine.
In addition to classes with instructors, you have to do a morning gymnastics complex every day, which includes special exercises with lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Relaxation and contraction of abdominal muscles.The initial position stands, his feet are separated -Swidth, the body's hands are lowered.Make a smooth breathing, relax the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.During breathing, pull into yourself as much as possible, tense the muscles of the press.Exercise must be repeated before the appearance of fatigue of light.
- Head movements by bending the spine.The initial position of the knee, resting on the floor out of the back, the back is straight.Slowly lift your head and bend in the back.To linger in this position for a few seconds, and then smoothly return to its original position.Repeat at least 10-12 times.
- "Pendulum".The initial position is lying behind, the arms along the body, the feet are bent at the right corner of the knee and hip joints.Turn the feet to the right and left with a swaying pendulum -shaped movement, trying to get the floor.At the same time, the shoulder knife cannot be torn from the floor.
- "Boat".The initial position lying in the stomach, hands reached forward.Torn the upper body and legs from the floor, bend behind.To linger in this position for 5-6 seconds and slowly return to the starting position.Do 10 times.
The consequences and complications that may occur
The main complications of lumbar osteochondrosis are:
- formation of intervertebral hernias;
- Dystonia Vegetovascular;
- SpondyLolis, Spondylolistz;
- osteoftosis;
- spondylarthrosis;
- Stenosis of the spinal cord, which leads to the compression of the spinal cord and is able to cause a loss of continuous work capacity and reduce the quality of life.
The long compression of the nervous roots that instead of certain organs from the abdominal cavity from time to time causes a decrease in function.As a result, patients have intestinal dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence) and pelvic organs (urination disorders, erectile dysfunction, frigidity, infertility).
Forecast
Pain syndrome for lumbar osteochondrosis takes place in the form of remission and exacerbation.Lumbago lasts 10-15 days, after that the patient's condition improves, the pain subsides.Secondary diseases of pharmularular can interfere with favorable results.Often, with lumbar osteochondrosis, there is a recurring pain attack, which every time becomes more intense and long.
In the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis complex, important roles include physiotherapy exercises.
Patients with severe lumbar osteochondrosis, with persistent pain and other manifestations are recognized as temporary defects.If within four months their condition does not improve, the problem of formation of disability groups is resolved.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of spinal osteochondrosis is the following steps:
- Smoking rejection;
- Normalization of weight;
- improvement of general physical conditions, active lifestyle;
- Avoiding provoking conditions (weight lifting, sharp movements, turns, tendencies).



















































