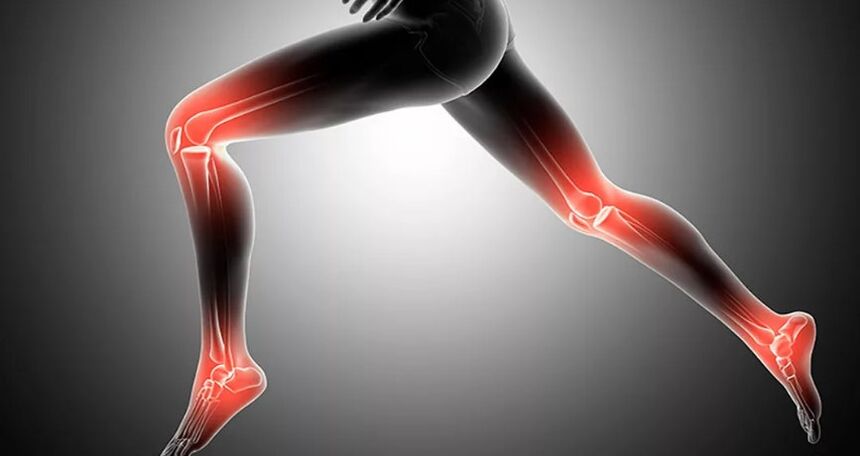
What is arthrosis?
- Karpal joints;
- lumbar spine and lumbar;
- knee joint;
- hip joint;
- shoulder joint;
- ankle joints;
- Metatarsophalangeal joint.
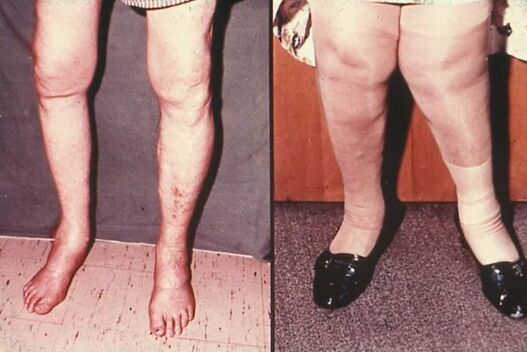
Possible consequences of arthrosis
Arthrosis type
- causes (primary and secondary forms);
- Arthrosis stages (three stages of development are classified);
- Pathology Localization (Place of Disease and Joint Types);
- Localization form (general and local form);
- The course of the disease (acute or chronic).
- acute form;
- chronic form.
Disease level
- The first level of the development of joint arthrosis is the initial phase of the disease. This is marked by a little cartilage tissue lesion and the loss of physiological function in collagen fibers. At the same time, at the first stage, minor morphological disorders of bone tissue and structural changes in synovial fluid are recorded. Joint cartilage is covered with cracks, the patient has a little pain in the pathology localization.
- The second level is the development of arthrosis with an increase in dynamics. This stage is marked by the appearance of stable pain, kroma. Morphological and dystrophic cartridges are important noted, during the diagnosis, bone growth is revealed. Osteofit is formed - Bone growth is seen during visual examination of the location of destruction. At the same time, the process of degenerative changes in synovial capsules occurs, which leads to its structural thinning. Diseases in this phase can often worsen and become regular. The pain gradually becomes constant.
- The third level is active development. At this stage, synovial fluid is almost absolutely no because of degeneration, and bone tissue suddenly -arriving with each other. Joint mobility is almost absent at all, the pain becomes more real. Cartilage tissue is also not there due to degenerative and atrophy changes. The third level treatment of joint arthrosis is considered impractical.
Causes of disease
- Traumatic damage to individual or all joints. This includes dislocation, broken bones, ligaments, meniscus rupture, wounds that penetrate. This reason is more common to people involved in sports, or whose activities are related to dangerous working conditions and physical activity;
- The inflammatory process is a factor that often acts as a secondary reason. Inflammation usually develops in patients suffering from gout, psoriasis, rheumatic disorders, autoimmune pathology. Joints are subject to patients at the exacerbation stage of infectious diseases, including tuberculosis, chlamydia, staphylococcus and other infectious diseases;
- Consequences of the form of breathing disease - flu, acute respiratory virus infections, acute respiratory infections;
- Increasing the patient's body weight - with disproportionate burden on their tissue joints, suffering from a constant mechanical effect, which leads to morphological deviations and destruction of cartilage structures;
- Excessive hypothermia that leads to the destruction of the integrity of cartilage tissue and the loss of synovial fluid structure;
- Thyroid disease.
Mechanism of disease development
Symptoms of arthrosis

- pain syndrome;
- crispy sound when moving;
- inactive or total decline in joint mobility;
- swelling;
- Joint conformation.



















































